Latest Developments in Antibody-Based Cancer immunotherapy – 2021 summary
May 8, 2022 Vered Ben-Hur Ph.DLatest Developments in Antibody-Based Cancer immunotherapy – 2021 summary
May 8, 2022
Vered Ben-Hur Ph.D
Targeted cancer therapy continues to evolve, and many new treatment combinations are being approved in addition to developmental advancements in novel checkpoint inhibitors. This article will address the lately approved antibody therapeutics (US and EU), those in regulatory review, the expanded approval of existing immunotherapies, and their associated companion diagnostics for cancer treatment. This article will address the following issues:
Antibody-Based Biopharmaceuticals Approved Between 2021-2022
Between 2021 to 2022, the FDA approved six new antibody-based immunotherapies and EMA five whereas four of the five accepted were previously cleared by the FDA, Table 12,3.
Table 1: Antibody therapeutics approved in the EU or US
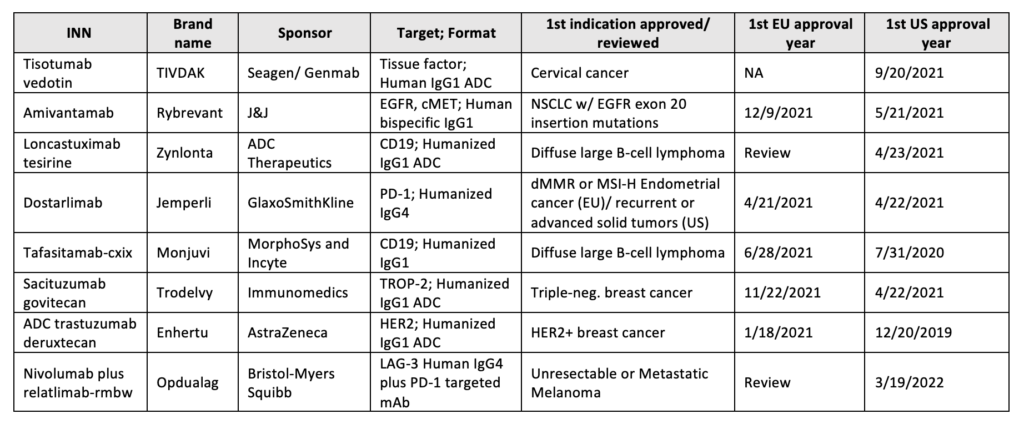
Starring 2021’s approval is Dostarlimab (Jemperli), anti-PD-1 Humanized IgG4, and Amivantamab (Rybrevant), a bispecific antibody targeting cancer epitopes, EGFR and MET. Both were approved in the EU (M.A. No. EU/1/21/1538/001) and US (BLA:761174/761210) to treat tumors with a high mutational burden and NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 mutations, respectively.
Companion Diagnostics and Future Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Approaches
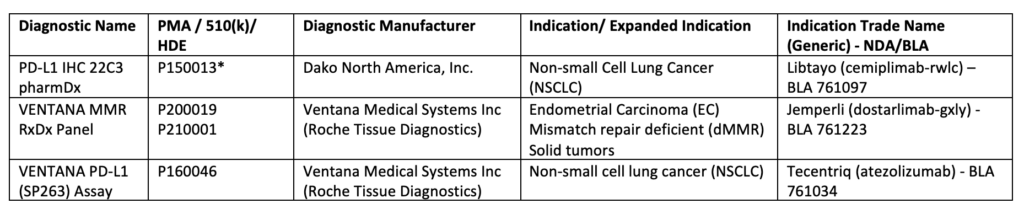
The use of immune signature to predict immunotherapeutic response led to an increase in the development and approval of immunohistochemical (IHC) diagnostic assays, Table 24. Such devices allow informative decision-making to assess tumor-favoring immune responsiveness5,6. For example, the VENTANA MMR RxDx panel was approved concomitantly with Dostarlimab (mentioned above) to distinguish the patients with dMMR who will benefit from this treatment7. Additional FDA-approved companion diagnostic tests are listed below, Table 2.
Table 2: List of Approved Companion Diagnostic Devices
In that regard, most IHC stained slides are visualized directly under a conventional light microscope or scanned and converted to digital slides that allow remote examination by a qualified pathologist. But alongside the manual assessment, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) -based software solutions as a Medical Device (SaMD) are being developed as promising approaches for fast, quantitative, and accurate pathologic assessment8,9. Thus, the demand for a clear regulatory framework to develop AI/ML-based SaMD has grown, and in 2021, the FDA released an action plan for a potential approach to premarket review (with a feedback request)10. In addition, 10 guiding principles that inform the development of Good Machine Learning Practice (GMLP) were written cooperatively with the Health Canada and the United Kingdom’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA)11. Although this developed technology is partially adopted in research use only (RUO) settings12, and its use in the clinic is mainly for observational studies8,9, AI will likely alter immunotherapy practice in the near future.
Expanded Indication Approvals
Important past year’s (2021) step in the immunotherapeutic approach is the expanded indication approvals for several already in-use drugs as adjuvant/neo-adjuvants therapies for the core axis PD-1/PD-L1. PD-1/PD-L1 blockade was proven to promote DFS (Disease-Free Survival) and EFS (Event-Free Survival). Atezolizumab (Tecentriq) had been cleared by the FDA as an adjuvant treatment with the companion diagnostic test VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263), mentioned above, for NSCLC (non-small-cell lung cancer) patients expressing PD-L113. Pembrolizumab (Kytruda) was approved both by EMA and FDA for the adjuvant treatment of RCC (Renal Cell Carcinoma) and neoadjuvant+adjuvant treatment for TNBC (Triple Negative Breast Cancer), respectively 14,15 . Nivolumab(Opdivo) has also been approved by the E.C. (European Commission) and the FDA for the adjuvant treatment of esophageal or GEJ (gastroesophageal junction) cancer16,17. The latter had also approved Nivolumab for adjuvant therapy of urothelial carcinoma18.
Latest Advancements in the Immunotherapy Field and 2022 Expected Approvals
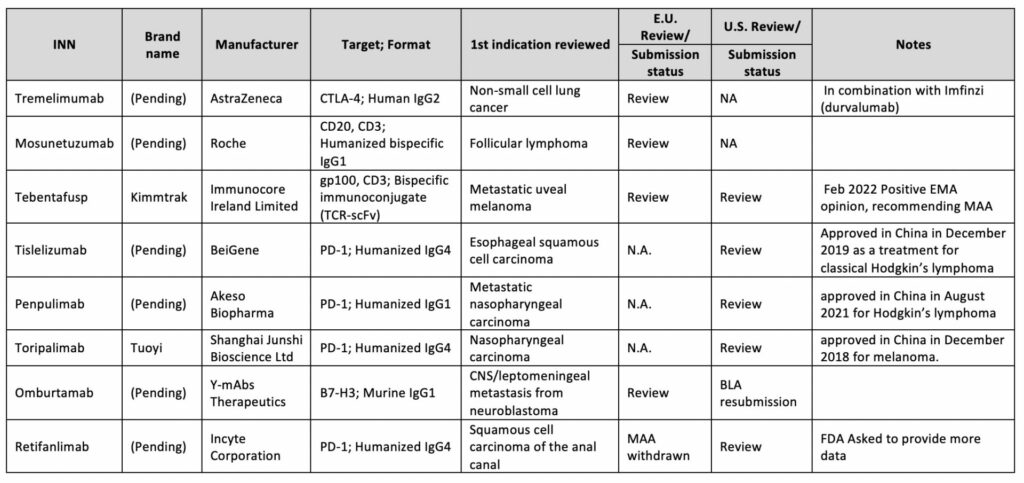
The Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs) to CTLA-4 and PD1/PDL1 is still at the top of the drug development pyramid. However, there have been recent advancements in understanding the mechanisms tumor cells exploit to evade the immune system19,20. Therefore, high hopes are pinned on additional immune and cancer-specific targets. The next wave of immunotherapies includes two promising immune inhibitory checkpoints, TIGIT (NCT03563716, NCT04570839, NCT04354246) and LAG3 (NCT03470922). The FDA recently approved LAG-3 inhibitory antibody as a first in class-fixed dose combination with PD-1 inhibitor (nivolumab), Table 1. This combination therapy established more than doubled median progression-free survival compared to the nivolumab arm. These results reinforce the growing perception that targeting two different immune checkpoints and other various types of combination therapy can be more beneficial than monotherapy. Additional expected submissions or approvals include CD137 (NCT01307267), OX40 (NCT02737475), CD20, BCMA, gp100 and EpCAM21,Table 3 2,3.
Table 3: 2022 expected approvals in EU or the US
Regulatory Perspective on mAbs Marketing Approval
From a regulatory point of view, the unexpected immune response of antibody-based biopharmaceuticals is one of the obstacles when developing biological products. Thus it is advised to navigate the strategic and regulatory decisions correctly to properly assess the safety and efficacy of such biotherapeutic 22. These assessments are usually conducted during pivotal clinical trials; as per ICH S6(R1), nonclinical immunogenicity data are not considered to be predictive of clinical safety 23. Even a greater challenge arises when designing antibody-based immunotherapy with expansion to dual targets i,e. Bispecific Antibodies (bsAbs). Such a strategy may increase immunogenicity issues which may also be related to novel complex structures. Consequently, for benefit-risk assessment, the FDA may request a comparison of the bsAb to an approved monospecific product directed against the same antigenic target(s)24.
In any circumstance, every applied BLA needs to show a clinical advantage. For example, FDA denied the approval of Retifanlimab (PD1-targeted mAb)25and Oportuzumab monatoxalso (EpCAM-targeted immunotoxin, ADC), questioning their clinical benefit. In addition, concerns were raised about the Oportuzumab monatoxalso company’s CMC (Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls) processes26.
Accelerated approvals are granted to many I.O. biologics; however, some are not reviewed for years. In 2021, FDA conducted an industry-wide evaluation of such drug approvals, which failed to meet post-marketing requirements 27,28. Following FDA’s call into question, several immunotherapy indications were withdrawn and removed from the US market28,29,30.
References
1. Cox EM, Edmund A V, Kratz E, Lockwood SH, Shankar A. Regulatory Affairs 101 : Introduction to Expedited Regulatory Pathways. 2020;2012:451-461. doi:10.1111/cts.12745
2. Www.antibodysociety.org.17Dec2021. Antibody therapeutics approved or in regulatory review in the EU or US. Antib Soc. Published online 2021. https://www.antibodysociety.org/resources/approved-antibodies/
3. Mullard A. 2021 FDA approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022;(January). doi:10.1038/d41573-022-00001-9
4. List of Cleared or Approved Companion Diagnostic Devices (In Vitro and Imaging Tools). doi:https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics/list-cleared-or-approved-companion-diagnostic-devices-in-vitro-and-imaging-tools
5. Emily A. Prince, PharmD1 ; Jenine K. Sanzari, PhD1 ; Dimple Pandya, MD1 ; David Huron P; and RE. Analytical Concordance of PD-L1 Assays Utilizing Antibodies From FDA-Approved Diagnostics in Advanced Cancers : A Systematic Literature Review abstract. Published online 2022. doi:10.1200/PO.20.00412
6. Christian U. Blank, John B. Haanen AR and TN. The cancer immunogram. Science (80- ). 2016;352(6286):658-660. doi:10.1126/science.aaf2834
7. VENTANA MMR RxDx Panel – P200019. Published 2021. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/recently-approved-devices/ventana-mmr-rxdx-panel-p200019
8. Baxi V, Edwards R, Montalto M, Saha S. Digital pathology and artificial intelligence in translational medicine and clinical practice. Mod Pathol. 2022;35(1):23-32. doi:10.1038/s41379-021-00919-2
9. Xu Z, Wang X, Zeng S, Ren X, Yan Y, Gong Z. Applying artificial intelligence for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(11):3393-3405. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.007
10. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Software as a Medical Device_Action Plan. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/software-medical-device-samd/artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning-software-medical-device
11. Good Machine Learning Practice for Medical Device Development: Guiding Principles. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/software-medical-device-samd/good-machine-learning-practice-medical-device-development-guiding-principles
12. Roche announces the release of its newest artificial intelligence (AI) based digital pathology algorithms to aid pathologists in evaluation of breast cancer markers, Ki-67, ER ,and PR. https://diagnostics.roche.com/global/en/news-listing/2021/roche-announces-release-of-its-newest-ai-based-digital-pathology-algorithms-to-aid-pathologists-in-evaluation-breast-cancer-markers-ki67-er-pr.html
13. FDA F and DA. FDA approves atezolizumab as an adjuvant treatment for non-small cell lung cancer. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-atezolizumab-adjuvant-treatment-non-small-cell-lung-cancer
14. FDA F and DA. FDA approves pembrolizumab for high-risk early-stage triple-negative breast cancer. Published 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-high-risk-early-stage-triple-negative-breast-cancer
15. EMA. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) adopted a positive opinion for the extension of Kytruda as monotherapy adjuvant treatment_RCC. Published 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/summaries-opinion/keytruda-6
16. Bristol Myers Squibb. Bristol Myers Squibb Receives European Commission Approval for Opdivo (nivolumab) as Adjuvant Treatment for Esophageal or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer Patients with Residual Pathologic Disease Following Chemoradiotherapy. Published 2021. https://news.bms.com/news/corporate-financial/2021/Bristol-Myers-Squibb-Receives-European-Commission-Approval-for-Opdivo-nivolumab-as-Adjuvant-Treatment-for-Esophageal-or-Gastroesophageal-Junction-Cancer-Patients-with-Residual-Pathologic-Disease-Following
17. Bristol Myers Squibb. U.S. Food and Drug Administration Accepts for Priority Review Application for Opdivo® (nivolumab) as Adjuvant Therapy for Patients with Resected Esophageal or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer. Published 2021. https://news.bms.com/news/details/2021/U.S.-Food-and-Drug-Administration-Accepts-for-Priority-Review-Application-for-Opdivo-nivolumab-as-Adjuvant-Therapy-for-Patients-with-Resected-Esophageal-or-Gastroesophageal-Junction-Cancer/default.aspx
18. FDA F and DA. FDA approves nivolumab for adjuvant treatment of urothelial carcinoma. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-nivolumab-adjuvant-treatment-urothelial-carcinoma
19. Kaplon H, Reichert JM. Antibodies to watch in 2021. MAbs. 2021;13(1). doi:10.1080/19420862.2020.1860476
20. Si Y, Melkonian AL, Curry KC, et al. Monoclonal antibody-based cancer therapies. Chinese J Chem Eng. 2021;30:301-307. doi:10.1016/j.cjche.2020.11.009
21. Vaddepally RK, Kharel P, Pandey R, Garje R. Review of Indications of FDA-Approved Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors per NCCN Guidelines with the Level of Evidence. :1-19.
22. Vandivort TC, Horton DB, Johnson SB. Regulatory and strategic considerations for addressing immunogenicity and related responses in biopharmaceutical development programs. J Clin Transl Sci. 2020;4(6):547-555. doi:10.1017/cts.2020.493
23. European Medicine Agency. EMA/CHMP/ICH/731268/1998 ICH guideline S6 (R1) on preclinical safety evaluation of biotechnology-derived pharmaceuticals. Comm Med Prod Hum use ICH. 2011;6(June):1-22. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-s6r1-preclinical-safety-evaluation-biotechnology-derived-pharmaceuticals-step-5_en.pdf
24. Gough J, Nettleton D. Bispecific Antibody Development Programs - Guidance for Industry_CEDER. Manag Doc Maz. 2019;(April):10.
25. Tucker N. FDA Denies Approval of Retifanlimab for Locally Advanced or Metastatic SCAC Subgroup. Published 2021. https://www.targetedonc.com/view/fda-denies-approval-of-retifanlimab-for-locally-advanced-or-metastatic-scac-subgroup
26. Biospace. FDA Slams Sesen Bio with CRL for Bladder Cancer Drug. Published 2021. https://www.biospace.com/article/fda-crushes-sesen-bio-with-crl-for-bladder-cancer-drug/
27. Astor L. FDA Cracks Down on Dangling Accelerated Approvals in 2021, Pathway Is Scrutinized. Published 2021. https://www.targetedonc.com/view/fda-cracks-down-on-dangling-accelerated-approvals-in-2021-pathway-is-scrutinized
28. FDA In Brief: FDA Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee to Review Status of Six Indications Granted Accelerated Approval. Published online 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/fda-brief/fda-brief-fda-oncologic-drugs-advisory-committee-review-status-six-indications-granted-accelerated
29. Merck withdraws Keytruda from SCLC indication amid FDA crackdown. Published 2021. https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/merck-withdraws-keytruda-for-lung-cancer-amid-fda-crackdown/
30. Nivolumab Indication in Small Cell Lung Cancer Withdrawn in U.S. Market. Published 2021. https://ascopost.com/issues/january-25-2021/nivolumab-indication-in-small-cell-lung-cancer-withdrawn-in-us-market/
This article was prepared by:

Vered Ben Hur. Ph.D
Pharma Regulation Projects Manager
For more information about our Pharmaceuticals industry visit:




